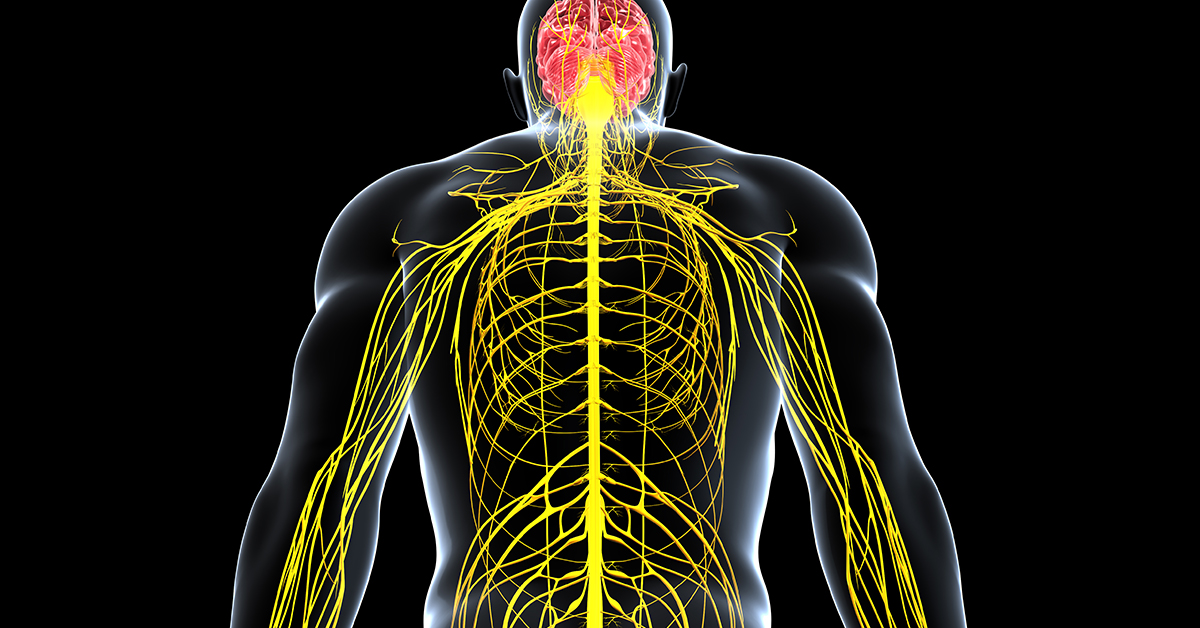
What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is a term that is used to describe damage to the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves that control sensation, muscle function and regulation of certain vital functions, such as heart rate and blood pressure. Damage to the peripheral nervous system can occur due to a number of causes.
Peripheral neuropathy commonly affects individuals who have risk factors and are above the age of 50 years.
What causes Peripheral Neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy is commonly caused by diabetes mellitus. It is rarely seen in the early stages of this disease and is commonly a sign of complicated diabetes mellitus. However, peripheral neuropathy can be caused by other conditions as well such as HIV, medications, high alcohol consumption, and even smoking. More rare causes include liver disease, kidney disease, blood cancer, such as lymphoma or myeloma, and certain neurological conditions such as Gillian Barre syndrome.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms include tingling, numbness and pain at the site of nerve involvement. In some cases, patients may lose sensation and even function of the small muscles.
Peripheral neuropathy can be a risk factor for developing infections in patients with diabetes. For example, the loss of sensation that occurs due to peripheral neuropathy involving the foot can make patients ignore any injury that may occur to the skin and superficial tissues. Normally, if an injury occurs, it is natural to want to clean the area and apply a bandage. However, as there is no sensation, the patient is unaware that there has been an injury and such measures may not be taken. This can cause the injury to become infected, and if left untreated, can cause severe sepsis.
Peripheral neuropathy is usually considered as a diagnosis in patients who have diabetes and have had problems sensing hot and cold or even sharp and blunt objects. Nerve conduction studies may be conducted to assess the conduction of nerve signals through the nerve fibers. Conduction of signals to the muscles, called electromyography, may also be performed. If diabetes is not the cause, an alternative diagnoses may need to be considered, and specific tests should be performed to ascertain the cause.
How is Peripheral Neuropathy treated?
If a patient is suffering from peripheral neuropathy, it is essential that they take care and avoid any injury. Adequate control of blood sugars in patients with diabetes is essential. Stopping smoking and reducing alcohol intake is important.
In cases where pain is a predominant symptom, painkillers can be offered to help. However, the medications that usually work best to ease pain are antidepressant medication and even anticonvulsant medication. Newer treatments such as Pregabalin are now available that can effectively control pain due to peripheral neuropathy.
In case complications such as foot ulcers or infections occur, antibiotics may be prescribed.